-
Sign In
-

-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
-
-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
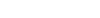
Pacific Blue™ anti-human CD107a (LAMP-1)
Antibodies Single
Sony
H4A3
Flow Cytometry
Mouse IgG1, κ
Human
Human adult adherent peripheral blood cells
2243120
$290.00
Description
CD107a, also known as Lysosome-Associated Membrane Protein 1 (LAMP-1) or LGP-120, is a 110-140 kD type I membrane glycoprotein. Mature CD107a is heavily glycosylated from a 40 kD core protein. This molecule is located on the luminal side of lysosomes. Upon activation, CD107a is transferred to the cell membrane surface of activated platelets, activated lymphocytes, macrophages, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and some tumor cells. CD107a has been suggested to play a role in the protection of lysosomal membrane from lysosomal hydrolases which is involved in cell adhesion and regulation of tumor metastasis, and mediates autoimmune disease progression. CD107a is a ligand for galaptin and E-selectin. Surface expression of LAMP-1 has been shown to correlate with CD8+ T cell and NK cell cytotoxicity.
Formulation
Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.Recommended Usage
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤ 2.0 microg per 106 cells in 100 microL volume or 100 microL of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Pacific Blue™ has a maximum emission of 455 nm when it is excited at 405 nm. Prior to using Pacific Blue™ conjugate for flow cytometric analysis, please verify your flow cytometer's capability of exciting and detecting the fluorochrome.
References
1. Misse D, et al. 1999. Blood 93:2454.
2. Furuta K, et al. 2001. Am. J. Pathol. 159:449. (IHC)
3. Watanabe A, et al. 2011. J. Biol. Chem. 286:10702. PubMed
4. Baron Gaillard CL, et al. 2011. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:5459. PubMed
5. Hauck CR and Meyer TF. 1997. FEBS Lett. 405:86. (IF, IP)
6. De Keersmaecker B, et al. 2012. J. Virol. 86:9351. PubMed
7. Knodler LA, et al. 2010. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 107:17733. (IF)
8. Oh J, et al. 2000. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9:375. (WB)
9. Salio M, et al. 2013 PNAS. 110:4753. PubMed