-
Sign In
-

-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
-
-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
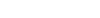
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-human CD163
Antibodies Single
Sony
GHI/61
Flow Cytometry
Mouse IgG1, κ
Human
2268095
$116.00
Description
CD163 is a member of the group B scavenger receptor cysteine-rich superfamily, also known as GHI/61, M130, RM3/1, p155, hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex receptor, or macrophage-associated antigen. It is a 134 kD (non-reduced)/155 kD (reduced) glycoprotein primarily expressed on macrophages, Kupffer cells, monocytes, a subset of dendritic cells, and a subset of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. CD163 binds to haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex and TWEAK, and plays a role in clearing hemoglobin and regulating cytokine production by macrophages. Membrane CD163 can be cleaved by metalloproteinases (MMP), resulting in a soluble form. Elevated serum level of sCD163 has been implicated in many kinds of inflammatory diseases.
Formulation
Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and 0.2% (w/v) BSA (origin USA).Recommended Usage
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 microL per million cells or 5 microL per 100 microL of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Alexa Fluor® 647 has a maximum emission of 668 nm when it is excited at 633 nm / 635 nm.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents.
References
1. Pulford K, et al. 1992. Immunology 75:588. (ICC, IP, WB)
2. Law SK, et al. 1993. Eur. J. Immunol. 23:2320.
3. Madsen M, et al. 2004. J. Biol. Chem. 279:51561.
4. Kim WK, et al. 2006. Am. J. Pathol. 168:822. (FC)
5. Buttari B, et al. 2011. Atherosclerosis. 215:316. PubMed