-
Sign In
-

-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
-
-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse Ki-67
Antibodies Single
Sony
16A8
Flow Cytometry
Rat IgG2a, κ
Human,Mouse
<em>E. coli</em> expressed partial mouse Ki-67 recombinant protein, 1816-2163 aa.
3862095
$145.00
Description
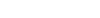
The nuclear protein Ki-67 was first identified by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67, which was generated by immunizing mice with nuclei of the L428 Hodgkin lymphoma cell line. Ki-67 protein plays an essential role in ribosomal RNA transcription and cell proliferation. Expression of Ki-67 occurs during G1, S, G2, and M phase, while in G0 phase the Ki-67 protein is not detectable. Ki-67 is strongly expressed in proliferating cells and has been reported as a prognostic marker in various tumors.
Formulation
Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.Recommended Usage
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by our Ki-67 staining protocol below. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.125 microg per million cells in 100 microL volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
* Alexa Fluor® 700 has a maximum emission of 719 nm when it is excited at 633 nm / 635 nm. Prior to using Alexa Fluor® 700 conjugate for flow cytometric analysis, please verify your flow cytometer's capability of exciting and detecting the fluorochrome.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents.