-
Sign In
-

-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
-
-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
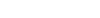
PE/Cy7 anti-human CD158e1 (KIR3DL1, NKB1)
Antibodies Single
Sony
DX9
Flow Cytometry
Mouse IgG1, κ
Human
Human NK cell clone VL186-1.6
2163600
$376.00
Description
CD158e1, also known as NKB1, is a 70 kD member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that is expressed on a subset of natural killer cells and T cells at varying levels among individuals. NKB1 is a type I membrane protein containing two immunoglobulin C2-type domains. The interaction of NKB1 with specific HLA-B antigens on a target cell (the HLA-Bw4 allele, for example) inhibits cytotoxicity and prevents target cell lysis and death. The interactions between KIR and MHC class I are thought to be important in NK and T cell regulation following antigen stimulation. The absence of ligands for KIRs may lower the threshold for activation through activating receptors and increase inflammation and susceptibility to autoimmune disease.
Formulation
Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and 0.2% (w/v) BSA (origin USA).Recommended Usage
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 microL per million cells or 5 microL per 100 microL of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
References
1. Litwin V, et al. 1994. J. Exp. Med. 180:537. (IP)
2. Gumperz J, et al. 1996. J. Exp. Med. 183:1817.
3. Gardiner CM, et al. 2001. J. Immunol. 166:2992.
4. Bakker ABH, et al. 1998. J. Immunol. 160:5239.
5. Goodier M, et al. 2000. J. Immunol. 165:139.
6. Kirwan SE and Burshtyn DN. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:5006. (FC)
7. Yawata M, et al. 2002. Immunogenetics 54:543.
8. Valiante NM, et al. 1997. Immunity 7:739.
9. Pascal V, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:1625. (FC) PubMed
10. Lichterfeld M, et al. 2008. J. Exp. Med. 204:2813. (FC) PubMed