-
Sign In
-

-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
-
-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
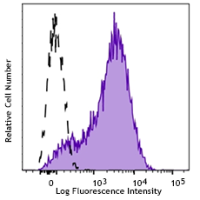
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-human CD279 (PD-1)
Antibodies Single
Sony
EH12.2H7
Flow Cytometry
Mouse IgG1, κ
Human,Non-human primate,Other
Human Ig cocktail
2249830
$468.00
Description
Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1), also known as CD279, is a 55 kD member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD279 contains the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) in the cytoplasmic region and plays a key role in peripheral tolerance and autoimmune disease. CD279 is expressed predominantly on activated T cells, B cells, and myeloid cells. PD-L1 (B7-H1) and PD-L2 (B7-DC) are ligands of CD279 (PD-1) and are members of the B7 gene family. Evidence suggests overlapping functions for these two PD-1 ligands and their constitutive expression on some normal tissues and upregulation on activated antigen-presenting cells. Interaction of CD279 ligands results in inhibition of T cell proliferation and cytokine secretion.
Formulation
Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).Recommended Usage
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents.
References
- Dorfman DM, et al. 2006 Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 30:802. (FA)
- Radziewicz H, et al. 2007. J. Virol. 81:2545. (FA)
- Velu V, et al. 2007. J. Virol. 81:5819. (FA)
- Zahn RC, et al. 2008. J. Virol. 82:11577. PubMed
- Chang WS, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:6707. (FC) PubMed
- Nakamoto N, et al. 2009. PLoS Pathog. 5:e1000313. (FA)
- Jones RB, et al. 2009. J. Virol. 83:8722. (FC) PubMed
- Vojnov L, et al. 2010. J. Virol. 84:753. (FC) PubMed
- Radziewicz H, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:2410. (FC) PubMed
- Monteriro P, et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 186:4618. PubMed
- Conrad J, et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 186:6871. PubMed
- Salisch NC, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:476. (Rhesus reactivity)
- Li H and Pauza CD. 2015. Eur. J. Immunol. 45:298. (IHC)
- Peterson VM, et al. 2017. Nat. Biotechnol. 35:936. (PG)