-
Sign In
-

-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
-
-
 Sony Biotechnology
Sony Biotechnology
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-human HLA-A,B,C
Antibodies Single
Sony
W6/32
Flow Cytometry
Mouse IgG2a, κ
Human
2157160
$457.00
Description
MHC class I antigens associated with β2-microglobulin are expressed by all human nucleated cells. MHC class I molecules are involved in presentation of antigens to CD8+ T cells. They play an important role in cell-mediated immune responses and tumor surveillance.
Formulation
Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA).Recommended Usage
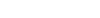
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤5 microL per million cells or 5 microL per 100 microL of whole blood. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
Brilliant Violet 605™ excites at 405 nm and emits at 603 nm. The bandpass filter 610/20 nm is recommended for detection, although filter optimization may be required depending on other fluorophores used. Be sure to verify that your cytometer configuration and software setup are appropriate for detecting this channel. Refer to your instrument manual or manufacturer for support. Brilliant Violet 605™ is a trademark of Sirigen Group Ltd.
This product is subject to proprietary rights of Sirigen Inc. and is made and sold under license from Sirigen Inc. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer a non-transferable right to use the purchased product for research purposes only. This product may not be resold or incorporated in any manner into another product for resale. Any use for therapeutics or diagnostics is strictly prohibited. This product is covered by U.S. Patent(s), pending patent applications and foreign equivalents.
References
1. Darrow TL, et al. 1989. J. Immunol. 142:3329.
2. Stern P, et al. 1987. J. Immunol. 138:1088.
3. Tran TM, et al. 2001. Immunogenetics 53:440.
4. Barbatis C, et al. 1981. Gut 22:985.
5. Ayyoub M, et al. 2004. Cancer Immunity 4:7.
6. DeFelice M, et al. 1990. Cell. Immunol. 126:420.
7. Fayen J, et al. 1998. Int. Immunol. 10:1347.
8. Turco MC, et al. 1988. J. Immunol. 141:2275.
9. Geppert TD, et al. 1989. J. Immunol. 142:3763.
10. Wooden SL, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:1383.
11. Nagano M, et al. 2007. Blood 110:151.
12. McLoughlin RM,et al.2008. J. Immunol. 181:1323. PubMed
13. Takahara M, et al.2008. J. Leukoc. Biol. 83:742. PubMed
14. Lunemann A, et al.2008. J. Immunol. 181:6170. PubMed
15. Laing BJ, et al. 2010. J. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 139:1402. PubMed
16. Yoshino N, et al. 2000. Exp. Anim. (Tokyo) 49:97. (FC)
17. Vambutas A, et al. 2000. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immun. 7:79.
18. Coppieters KT, et al. 2012. J. Exp. Med. 209:51. (epitope)
19. Crivello P, et al. 2013. Hum Immunol. 22:100. PubMed
20. Jung Y, et al. 2015. Mol Cancer Res. 13:197. PubMed